How to Design Effective Research Questionnaires for Robust Findings

As a staple in data collection, questionnaires help uncover robust and reliable findings that can transform industries, shape policies, and revolutionize understanding. Whether you are exploring societal trends or delving into scientific phenomena, the effectiveness of your research questionnaire can make or break your findings.
In this article, we aim to understand the core purpose of questionnaires, exploring how they serve as essential tools for gathering systematic data, both qualitative and quantitative, from diverse respondents. Read on as we explore the key elements that make up a winning questionnaire, the art of framing questions which are both compelling and rigorous, and the careful balance between simplicity and depth.
The Role of Questionnaires in Research
So, what is a questionnaire? A questionnaire is a structured set of questions designed to collect information, opinions, attitudes, or behaviors from respondents. It is one of the most commonly used data collection methods in research. Moreover, questionnaires can be used in various research fields, including social sciences, market research, healthcare, education, and psychology. Their adaptability makes them suitable for investigating diverse research questions.
Questionnaire and survey are two terms often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings in the context of research. A survey refers to the broader process of data collection that may involve various methods. A survey can encompass different data collection techniques, such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and yes, questionnaires.
Pros and Cons of Using Questionnaires in Research:
While questionnaires offer numerous advantages in research, they also come with some disadvantages that researchers must be aware of and address appropriately. Careful questionnaire design, validation, and consideration of potential biases can help mitigate these disadvantages and enhance the effectiveness of using questionnaires as a data collection method.

Structured vs Unstructured Questionnaires
Structured Questionnaire:
A structured questionnaire consists of questions with predefined response options. Respondents are presented with a fixed set of choices and are required to select from those options. The questions in a structured questionnaire are designed to elicit specific and quantifiable responses. Structured questionnaires are particularly useful for collecting quantitative data and are often employed in surveys and studies where standardized and comparable data are necessary.
Advantages of Structured Questionnaires:
- Easy to analyze and interpret: The fixed response options facilitate straightforward data analysis and comparison across respondents.
- Efficient for large-scale data collection: Structured questionnaires are time-efficient, allowing researchers to collect data from a large number of respondents.
- Reduces response bias: The predefined response options minimize potential response bias and maintain consistency in data collection.
Limitations of Structured Questionnaires:
- Lack of depth: Structured questionnaires may not capture in-depth insights or nuances as respondents are limited to pre-defined response choices. Hence, they may not reveal the reasons behind respondents’ choices, limiting the understanding of their perspectives.
- Limited flexibility: The fixed response options may not cover all potential responses, therefore, potentially restricting respondents’ answers.
Unstructured Questionnaire:
An unstructured questionnaire consists of questions that allow respondents to provide detailed and unrestricted responses. Unlike structured questionnaires, there are no predefined response options, giving respondents the freedom to express their thoughts in their own words. Furthermore, unstructured questionnaires are valuable for collecting qualitative data and obtaining in-depth insights into respondents’ experiences, opinions, or feelings.
Advantages of Unstructured Questionnaires:
- Rich qualitative data: Unstructured questionnaires yield detailed and comprehensive qualitative data, providing valuable and novel insights into respondents’ perspectives.
- Flexibility in responses: Respondents have the freedom to express themselves in their own words. Hence, allowing for a wide range of responses.
Limitations of Unstructured Questionnaires:
- Time-consuming analysis: Analyzing open-ended responses can be time-consuming, since, each response requires careful reading and interpretation.
- Subjectivity in interpretation: The analysis of open-ended responses may be subjective, as researchers interpret and categorize responses based on their judgment.
- May require smaller sample size: Due to the depth of responses, researchers may need a smaller sample size for comprehensive analysis, making generalizations more challenging.
Types of Questions in a Questionnaire
In a questionnaire, researchers typically use the following most common types of questions to gather a variety of information from respondents:
1. Open-Ended Questions:
These questions allow respondents to provide detailed and unrestricted responses in their own words. Open-ended questions are valuable for gathering qualitative data and in-depth insights.
Example: What suggestions do you have for improving our product?
2. Multiple-Choice Questions
Respondents choose one answer from a list of provided options. This type of question is suitable for gathering categorical data or preferences.
Example: Which of the following social media/academic networking platforms do you use to promote your research?
- ResearchGate
- Academia.edu
3. Dichotomous Questions
Respondents choose between two options, typically “yes” or “no”, “true” or “false”, or “agree” or “disagree”.
Example: Have you ever published in open access journals before?
- Yes
- No
4. Scaling Questions
These questions, also known as rating scale questions, use a predefined scale that allows respondents to rate or rank their level of agreement, satisfaction, importance, or other subjective assessments. These scales help researchers quantify subjective data and make comparisons across respondents.
There are several types of scaling techniques used in scaling questions:
i. Likert Scale:
The Likert scale is one of the most common scaling techniques. It presents respondents with a series of statements and asks them to rate their level of agreement or disagreement using a range of options, typically from “strongly agree” to “strongly disagree”.For example: Please indicate your level of agreement with the statement: “The content presented in the webinar was relevant and aligned with the advertised topic.”
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Neutral
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
ii. Semantic Differential Scale:
The semantic differential scale measures respondents’ perceptions or attitudes towards an item using opposite adjectives or bipolar words. Respondents rate the item on a scale between the two opposites. For example:
- Easy —— Difficult
- Satisfied —— Unsatisfied
- Very likely —— Very unlikely
iii. Numerical Rating Scale:
This scale requires respondents to provide a numerical rating on a predefined scale. It can be a simple 1 to 5 or 1 to 10 scale, where higher numbers indicate higher agreement, satisfaction, or importance.
iv. Ranking Questions:
Respondents rank items in order of preference or importance. Ranking questions help identify preferences or priorities.
Example: Please rank the following features of our app in order of importance (1 = Most Important, 5 = Least Important):
- User Interface
- Speed
- Functionality
- Customer Support
- Cost
By using a mix of question types, researchers can gather both quantitative and qualitative data, providing a comprehensive understanding of the research topic and enabling meaningful analysis and interpretation of the results. The choice of question types depends on the research objectives, the desired depth of information, and the data analysis requirements.
Methods of Administering Questionnaires
There are several methods for administering questionnaires, and the choice of method depends on factors such as the target population, research objectives, convenience, and resources available. Here are some common methods of administering questionnaires:

Each method has its advantages and limitations. Online surveys offer convenience and a large reach, but they may be limited to individuals with internet access. Face-to-face interviews allow for in-depth responses but can be time-consuming and costly. Telephone surveys have broad reach but may be limited by declining response rates. Researchers should choose the method that best suits their research objectives, target population, and available resources to ensure successful data collection.
How to Design a Questionnaire
Designing a good questionnaire is crucial for gathering accurate and meaningful data that aligns with your research objectives. Here are essential steps and tips to create a well-designed questionnaire:
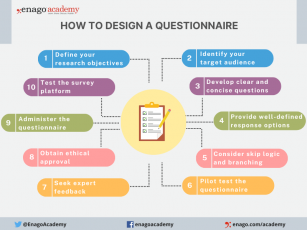
1. Define Your Research Objectives: Clearly outline the purpose and specific information you aim to gather through the questionnaire.
2. Identify Your Target Audience: Understand respondents’ characteristics and tailor the questionnaire accordingly.
3. Develop the Questions:
- Write Clear and Concise Questions
- Avoid Leading or Biasing Questions
- Sequence Questions Logically
- Group Related Questions
- Include Demographic Questions
4. Provide Well-defined Response Options: Offer exhaustive response choices for closed-ended questions.
5. Consider Skip Logic and Branching: Customize the questionnaire based on previous answers.
6. Pilot Test the Questionnaire: Identify and address issues through a pilot study.
7. Seek Expert Feedback: Validate the questionnaire with subject matter experts.
8. Obtain Ethical Approval: Comply with ethical guidelines, obtain consent, and ensure confidentiality before administering the questionnaire.
9. Administer the Questionnaire: Choose the right mode and provide clear instructions.
10. Test the Survey Platform: Ensure compatibility and usability for online surveys.
By following these steps and paying attention to questionnaire design principles, you can create a well-structured and effective questionnaire that gathers reliable data and helps you achieve your research objectives.
Characteristics of a Good Questionnaire
A good questionnaire possesses several essential elements that contribute to its effectiveness. Furthermore, these characteristics ensure that the questionnaire is well-designed, easy to understand, and capable of providing valuable insights. Here are some key characteristics of a good questionnaire:
1. Clarity and Simplicity: Questions should be clear, concise, and unambiguous. Avoid using complex language or technical terms that may confuse respondents. Simple and straightforward questions ensure that respondents interpret them consistently.
2. Relevance and Focus: Each question should directly relate to the research objectives and contribute to answering the research questions. Consequently, avoid including extraneous or irrelevant questions that could lead to data clutter.
3. Mix of Question Types: Utilize a mix of question types, including open-ended, Likert scale, and multiple-choice questions. This variety allows for both qualitative and quantitative data collections.
4. Validity and Reliability: Ensure the questionnaire measures what it intends to measure (validity) and produces consistent results upon repeated administration (reliability). Validation should be conducted through expert review and previous research.
5. Appropriate Length: Keep the questionnaire’s length appropriate and manageable to avoid respondent fatigue or dropouts. Long questionnaires may result in incomplete or rushed responses.
6. Clear Instructions: Include clear instructions at the beginning of the questionnaire to guide respondents on how to complete it. Explain any technical terms, formats, or concepts if necessary.
7. User-Friendly Format: Design the questionnaire to be visually appealing and user-friendly. Use consistent formatting, adequate spacing, and a logical page layout.
8. Data Validation and Cleaning: Incorporate validation checks to ensure data accuracy and reliability. Consider mechanisms to detect and correct inconsistent or missing responses during data cleaning.
By incorporating these characteristics, researchers can create a questionnaire that maximizes data quality, minimizes response bias, and provides valuable insights for their research.
Conclusion
In the pursuit of advancing research and gaining meaningful insights, investing time and effort into designing effective questionnaires is a crucial step. A well-designed questionnaire is more than a mere set of questions; it is a masterpiece of precision and ingenuity. Each question plays a vital role in shaping the narrative of our research, guiding us through the labyrinth of data to meaningful conclusions. Indeed, a well-designed questionnaire serves as a powerful tool for unlocking valuable insights and generating robust findings that impact society positively.
Have you ever designed a research questionnaire? Reflect on your experience and share your insights with researchers globally through Enago Academy’s Open Blogging Platform. Join our diverse community of 1000K+ researchers and authors to exchange ideas, strategies, and best practices, and together, let’s shape the future of data collection and maximize the impact of questionnaires in the ever-evolving landscape of research.
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions
A research questionnaire is a structured tool used to gather data from participants in a systematic manner. It consists of a series of carefully crafted questions designed to collect specific information related to a research study.
Questionnaires play a pivotal role in both quantitative and qualitative research, enabling researchers to collect insights, opinions, attitudes, or behaviors from respondents. This aids in hypothesis testing, understanding, and informed decision-making, ensuring consistency, efficiency, and facilitating comparisons.
Questionnaires are a versatile tool employed in various research designs to gather data efficiently and comprehensively. They find extensive use in both quantitative and qualitative research methodologies, making them a fundamental component of research across disciplines. Some research designs that commonly utilize questionnaires include:
a) Cross-Sectional Studies b) Longitudinal Studies
c) Descriptive Research
d) Correlational Studies e) Causal-Comparative Studies
f) Experimental Research g) Survey Research
h) Case Studies i) Exploratory Research
A survey is a comprehensive data collection method that can include various techniques like interviews and observations. A questionnaire is a specific set of structured questions within a survey designed to gather standardized responses. While a survey is a broader approach, a questionnaire is a focused tool for collecting specific data.
The choice of questionnaire type depends on the research objectives, the type of data required, and the preferences of respondents. Some common types include:
• Structured Questionnaires: These questionnaires consist of predefined, closed-ended questions with fixed response options. They are easy to analyze and suitable for quantitative research. • Semi-Structured Questionnaires: These questionnaires combine closed-ended questions with open-ended ones. They offer more flexibility for respondents to provide detailed explanations.
• Unstructured Questionnaires: These questionnaires contain open-ended questions only, allowing respondents to express their thoughts and opinions freely. They are commonly used in qualitative research.
Following these steps ensures effective questionnaire administration for reliable data collection:
• Choose a Method: Decide on online, face-to-face, mail, or phone administration. • Online Surveys: Use platforms like SurveyMonkey
• Pilot Test: Test on a small group before full deployment • Clear Instructions: Provide concise guidelines
• Follow-Up: Send reminders if needed









![What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-73.png)
Thank you, Riya. This is quite helpful. As discussed, response bias is one of the disadvantages in the use of questionnaires. One way to help limit this can be to use scenario based questions. These type of questions may help the respondents to be more reflective and active in the process.
Thank you, Dear Riya. This is quite helpful.
Great insights there Doc