Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation

In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights. Researchers often struggle to pick the best method of data analysis because not all analytical approaches are equal when interpreting data. This is where content analysis and thematic analysis prove invaluable. These methodologies help systematically organize and interpret data to uncover subtle themes and patterns, transforming volumes of texts into impactful findings when applied skillfully.
What Is Content Analysis?
Content analysis is defined as a data analysis method that adopts a systematic approach to examine textual, visual, or verbal communication data. Quantifying words, concepts, themes, phrases, characters, or sentences within a dataset helps draw meaningful conclusions from the information. This approach uncovers how often certain information appears, giving insights into the context and content of communication.
Example of content analysis: Analyze terms like “sustainability” and associated words (e.g., “quality”) in online reviews to understand how consumers weigh environmental concerns against product attributes.
What Is Thematic Analysis?
Thematic analysis involves identifying, analyzing, and reporting themes or patterns within qualitative data. It emphasizes broad themes from different sources that represent fundamental aspects of a phenomenon.
Example of thematic analysis: In a study on student feedback, codes such as satisfaction and frustration were grouped into themes of positive and negative experiences, offering insights into overall perceptions of educational quality.
Similarities and Differences Between Content Analysis and Thematic Analysis
Content analysis and thematic analysis are two qualitative data analysis approaches that share some key similarities. They both involve examining written information by breaking down the text into smaller content units. Despite employing distinct approaches, their shared objective is to generate fresh insights and knowledge from qualitative data sources. Both methods require a comprehensive understanding of the data through an iterative process. Using these methods, theoretical claims in the research can be made.
To gain a comprehensive understanding of the applications of content analysis and thematic analysis, it’s beneficial to explore their differences.
| Point of Difference | Content Analysis | Thematic Analysis |
| Aim of the approach | Emphasis on frequency of category occurrences | Identifying recurring themes and cohesive analysis |
| Researcher’s focus | Analysis of content and relationships between variables | Exploration and interpretation of specific research question |
| Process of data analysis | Utilizes predefined categories and coding schemes | Iteratively coded and analyzed, flexible approach |
| Presentation of findings | Results often presented as conceptual maps or models | Themes with supporting excerpts presented in the final report |
| Interpretation quality | More objective approach with quantifiable data-driven analysis | Higher level of interpretation and subjective analysis |
Given these key differences and similarities, it is crucial for researchers to understand both these aspects to select the most appropriate approach based on their research questions, data characteristics, and goals. Making an informed choice allows one to employ the technique that will best elucidate insights, generate new knowledge, and align with the overall research aims. Recognizing their nuances is key to unlocking their full potential for precise data interpretation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Content Analysis and Thematic Analysis
By conducting a thoughtful evaluation of the pros and cons of both the methods, we can decide on which method to opt for. Here are the advantages and disadvantages of content analysis and thematic analysis:
| Data Analysis Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Content Analysis | 1. Direct examination of communication using text
2. Can be used for both, qualitative and quantitative analysis 3. Instrumental for historical and cultural insights 4. Closeness to data, including statistical analysis |
1.Time-consuming, notably with large data
2. Increased error, specially in relational analysis 3. Insufficient theoretical foundation constrains depth 4. Inherently reductive when dealing with complex texts |
| Thematic Analysis | 1. Flexibility in research design
2. Suitable for large datasets 3. Reliable coding, especially in teams 4. Applicable to broader research questions |
1. Potential to miss nuanced data
2. Complexity for novice researchers 3. Limited interpretation without theoretical model 4. Challenges in keeping data continuity |
Choosing the Right Method for Data Analysis: Content analysis or thematic analysis
Qualitative research relies on extracting meaning from complex data. However, not all analytical approaches are created equal. Researchers must select methods strategically based on the requirement of their research study. They need to understand the key differences between both the approached right from the research design stage. This knowledge guides the choice of optimal data analysis method aligned to the study goals. It helps researchers gain clarity regarding the technique to employ.
An insightful interpretation begins with the right analytical lens. By distinguishing approaches early on, researchers give themselves the best chance to unveil the crux of the data – paving the way for impactful qualitative discoveries.
How to Conduct Content Analysis
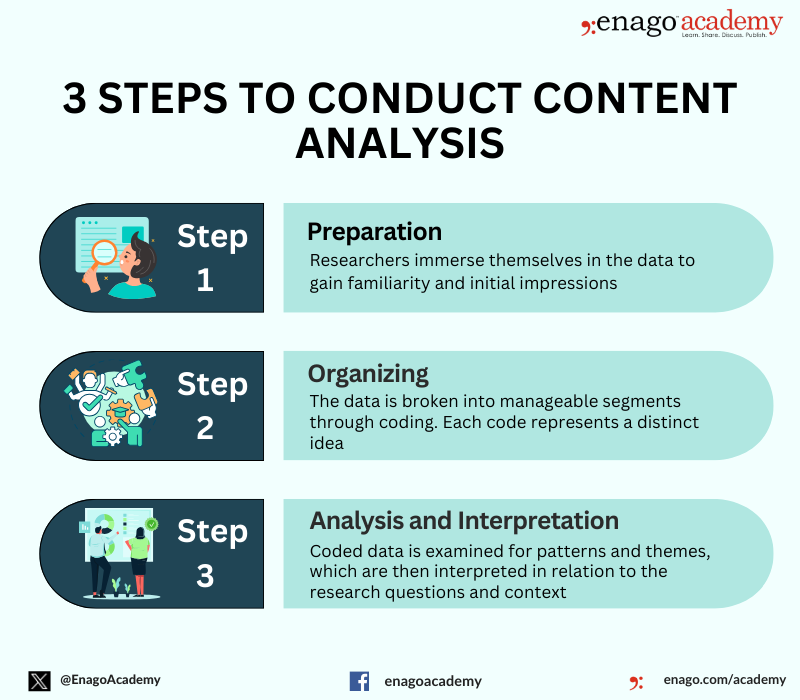
To fully unlock the potential of content analysis in understanding and comprehending data, researchers must follow systematic steps. Here are the steps for conducting content analysis:
How to Conduct Thematic Analysis
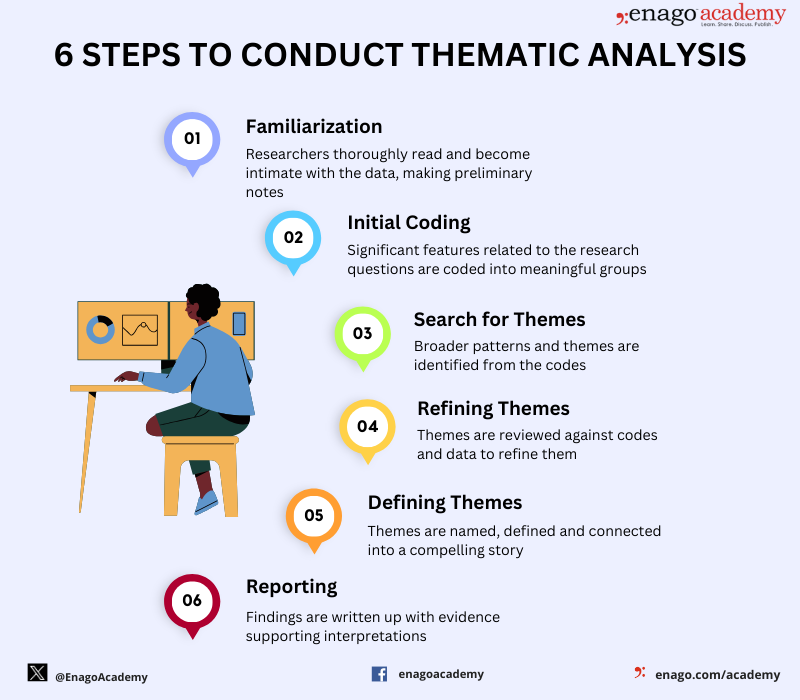
After deciding to employ thematic analysis, you can follow the six-step process for conducting thematic analysis outlined by Braun and Clarke.
Regardless of the data analysis method, it is crucial to grasp the functioning of both these approaches. This understanding enables you to make an informed decision about the most suitable method and accelerates your research process. Are you struggling to decide which is the best data analysis method for your research? Seek professional assistance for informed decisions and a smoother research journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
Content analysis quantifies and analyzes specific words, themes, or concepts within qualitative data, facilitating meaningful insights.
Thematic analysis serves the purpose of identifying significant patterns, or themes, within data, with the aim of addressing research objectives.
The main difference between content analysis and thematic analysis lies in their approach towards a dataset. Content analysis focuses on determining the frequency of categories, while thematic analysis the aim is to identify themes and organize the analysis cohesively.
The main stages of thematic analysis include: familiarization, initial coding, search for themes, refining themes, defining themes, and reporting.
The main stages of content analysis include: preparation, organization, analysis and interpretation.











informative site, I would like to be updated.