Affect Vs. Effect — Which one to use when? Know the difference!

Oh! How did I make such a silly blunder! That too in a research article which was reviewed and re-reviewed before we were pretty sure to submit! I was supposed to propose an effect of the indicator on the system and not the affected indicator on the system! Affect, Effect… Why are they so similar and misleading? What a fiasco!
Language is a very specific tool in research publishing. It helps researchers gain the common understanding of content. Moreover, usage of words could change within the context of very specific conditions (research design, statistical analysis), but the reader may observe variations in word usage and meaning across research disciplines.
Most Commonly Confused Words
Among many researchers in the English language whose usage can confuse both native and nonnative speakers (e.g., fewer vs. less; infer vs. imply), the concepts of affect and effect are particularly vexing. Most common, affect refers to action and is used as a verb. Merriam-Webster offers influence as a synonym for affect. In contrast, effect is most often used as a noun, usually indicating a result. But effect can also be a verb, as in “to effect change.”
Therefore, affect vs. effect is a most commonly confused issue. The problem arises because of its similarity in pronunciation, and especially when both the words are related to change. However, grammatically –
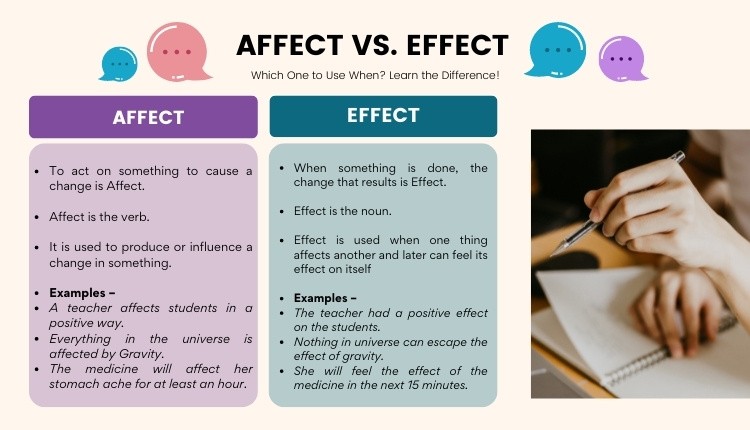
- Affect in a sentence, as a verb, describes the act of producing a change in someone or something.
- Effect in a sentence, as a noun, refers to a change that results when something is done or happens.
Affect Vs. Effect
Use of Affect
Affect is typically a transitive verb and is always used with an object, which means you will always include the name of the person or thing being affected.
Example of Affect:
The speed of the reaction was affected by the temperature.
When affect is used as a noun, it can refer to visible emotional response
Example of Affect:
The woman’s facial affect indicated that she was distressed by the conversation.
Use of Effect
Effect is typically a noun, which means the result or consequences of a cause or action. The word is often used with an adjective
Example of Effect:
The quality of food has a major effect on the state.
When effect is used as a verb, it means “cause something to come to being.” It is used when followed by the word “change.”
Example of Effect:
The biology research group effected change through peaceful discussions.
How to Identify the Usage of Effect and Affect?
- The RAVEN (Remember Affect is a Verb — Effect is a Noun) trick is quite famous to remember the difference between effect and affect and identify it.
- Verbs are actions and actions starts with A, and affect is a verb.
- When you do not know how to use affect as a verb, choose a synonym like impact or choose a more specific verb. For example, the weather affected her holiday plans can instead be written as — The weather ruined her holiday plans.
- You could use a grammatical article before nouns, so try identifying the noun effect with an article.
- Use another interesting tip — Accident & Emergency. When you are affected by an accident, the effect is an emergency.
- For every grammar rule, there is an exception. Effect vs. affect has an exception. Affect can be used as a noun when one talks about mood that someone appears to have. Effect can be used as a verb that essentially means “to bring about” or “to accomplish.”
Differentiating Affect Vs. Effect While Writing Your Research
In the aim of a research study, a researcher can describe or observe a particular chain of events, in many cases the investigator wishes to test a specific hypothesis — to determine how a particular situation, behavior, or context affects another. Furthermore, it is common for the hypothesis to specify an independent variable (X) and how it affects the dependent variable (Y). At this point, the investigator is proposing an effect (noun) or outcome that is the result of the ways in which X affects Y.
Once decisions about measurement and definition of X and Y are resolved, the choice of an appropriate statistical analysis further specifies the concept and scope of the proposed effect (noun). Effect in this context describes and quantifies the statistical probability that X is associated with a change in Y. It is a probability, not a certainty. Study designs that incorporate controlled observation methods (e.g., randomized controlled trials) increase the likelihood that the observed results are not due to other factors.
The best way to deal with the confusion in usage of words is to get a thorough grammar check done before any submission. Moreover, there are tools that can run a test, they are easy to access and are less time-consuming, giving reliable results to avoid grammar and language blunders, if any.
Have you ever gotten confused between effect and affect? Are there any other words that mean different but are spelled or pronounced similarly? Write to us or mention in the comments below about how you deal with such honest language err.
Frequently Asked Questions
"Affect" is commonly used as a verb, meaning to influence or produce a change. "Effect" is primarily used as a noun, representing the result or consequence of an action. However, "effect" can also be used as a verb, meaning to bring about or accomplish something.
"Here are some differences between ""affect"" and ""effect"":
1. The word ""affect"" is a verb, used to describe an action, while ""effect"" is a noun, used to describe a thing or result.
2. Both ""affect"" and ""effect"" relate to consequences and results, but their difference lies in their word class (verb versus noun).
3. In most cases, you will encounter ""affect"" as a verb and ""effect"" as a noun in closely related scenarios involving actions and their consequences. "
"To use ""affect"" and ""effect"" correctly, consider the following guidelines:
Affect (verb):
Use ""affect"" as a verb when you want to describe the action of influencing or producing a change in something or someone.
Effect (noun):
Use ""effect"" as a noun when you want to refer to the result, consequence, or outcome of something.
Effect (verb):
Use ""effect"" as a verb when you want to express bringing about or accomplishing something. "
"""affect"" and ""effect"" can be used as follows:
""Affect"" (as a verb):
""The teacher's instructional methods positively affect students' academic performance.""
In this sentence, ""affect"" is used as a verb to describe how the teacher's teaching approaches influence or impact the students' academic performance in a positive manner.
""Effect"" (as a noun):
""The research study found a significant effect of sleep deprivation on cognitive function.""
Here, ""effect"" is used as a noun to indicate the result or outcome of sleep deprivation on cognitive function, as observed in the research study."










Helped me very much to understand the differences between affect and effect meanings. Very helpful.
This helped me very much to rember the differences between them….. RAVEN…..ACCIDENT & EMERGENCY
This helped me very much to remeber the differences between them….. RAVEN…..ACCIDENT & EMERGENCY
Very good information and helpful. Like the RAVEN and different meaning’s between affect vs effect.
Thank you for the help, I am still trying to understand the difference between the two but will ALWAYS remember R.A.V.E.N
Simply remeber this: “‘a’ is for action”
Would this be correct ?
Were you affected by the flooding ?
The flooding had a bad effect on people .