The Effects of Recession on Research: 6 strategies to counter the challenges

Three years after the pandemic paralyzed the world, its aftermath continues to make the world go frenzy as the siren of recession rings louder with time. The current recession alert has alarmed several industries, including scientific research. The pandemic has led to a reduction in the number of new projects and a diversion of funds toward virology and vaccine research. This had a negative impact on the research outside the field concerning virology and life sciences at large. With several countries dipped in recession, experts have predicted a moderate recession this year due to the growing economic uncertainty. Although research was promised a boost in 2023, the scientific community is concerned about the effects of recession on research funding.
A recession can significantly impact research funding due to its effects on the economy and allocation of resources. The previous financial crisis had detrimental effects on research funding, resulting in a slowdown in the pace of research. Furthermore, the economic downturn in 2011 witnessed a drop in funding by key players in biomedical research, leading to the suspension of several projects.
Is academia immune to recession?
The cutbacks in research funding make research less immune to recession. Though funding and grants do not directly produce science, they influence the researchers and the technicians in delivering quality output. Additionally, industries cut down the funds for research, which decreases the knowledge output through industrial research. Therefore, decreased funding during a recession can result in an overall reduction in scientific output.
However, the recession of 2008 witnessed a positive impact on academia when it drove students to enroll in PhD programs and pursue their careers in research. It can be assumed that the decline in the rate of employment prompted many students to enroll in a PhD. Academia, considered more stable than the business sector, attracts talented individuals during periods of recession. Consequently, the increase in the enrollment in PhD programs resulted in a surge of research publications in that decade. Nonetheless, despite the resilience of academic research to recession, the overall impact of the economic downfall on research cannot be overlooked.
The Impact of Recession on Research
Research is affected during a recession due to the decrease in funding. Various funding agencies support research by providing grants that contribute to the development of research. The different sources of funding are:
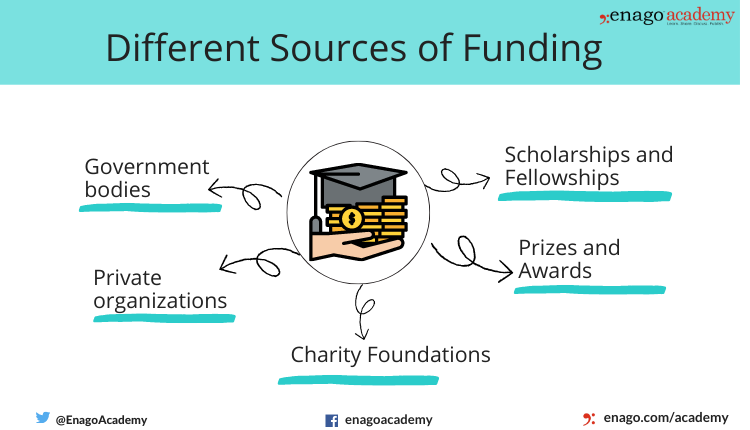
Recession affects research due to decrease in the budget for the grants. The different impacts of a recession on research are:
1. Budget cuts
The government may issue budget cuts, resulting in a decreased allotment of funds for research. Additionally, the government may restructure its priorities and divert available funds to areas like healthcare, economy, and defense, thereby reducing funds for other areas of research. There is also an increased chance of redirecting funds to projects that can offer immediate returns. The previous recession witnessed an enormous cut in funding by the National Institute of Health (NIH), which froze several projects.
2. Effects on the ongoing studies
The decrease in funding can terminate or halt an ongoing project. In clinical studies involving patients, this can lead to a downfall and leave negative impacts on the participants of the study. Restarting such studies can be very difficult and would be strenuous as it would demand more resources.
3. Reduced philanthropic contribution
Philanthropic organizations, charities, and trusts play a major role in research funding. It is reported that industrial and charitable sources play a significant role in biomedical research. Projects funded by these philanthropic organizations can take a hit during a recession due to a decrease in fundraisers and donations. Additionally, the organizations tend to divert their disposable income to charitable organizations.
4. Industry cutbacks
Industries may cut down their funds for research and development (R&D). Although life sciences companies, especially pharma companies, are known to be recession-proof, they may face financial difficulties in funding research. This can result in reduced funding for collaborative projects between academic institutions and industries, thereby limiting opportunities for research.
5. Increased competition for funding
Researchers may be crippled due to the difficulty in securing research grants, making their career prospects bleak. The lack of raise in salaries for staff and even termination of many staff and technicians can hinder the progress of a project. Apart from this, there would be increased competition within the scientific community to sustain their research projects and secure grants, which can open door for increasing misconduct. Additionally, increased competition can heighten scrutiny in the grant-reviewing process, making it challenging for researchers. It can also increase the risk of scientific misconduct among researchers.
6. Lack of stability
Limited funding can result in limited resources, and can this be less appealing for a researcher? The lack of resources can pose a limitation for researchers, influencing them to explore other options and migrate to other places. This may result in an increase in short-term contracts and temporary employment, resulting in a lack of stability in their career. Furthermore, institutes may implement freezing or downsizing measures. This can limit the employment prospects for researchers and academicians. Furthermore, with limited resources, it would be difficult to attract and retain talented minds.
Undoubtedly, a recession hinders the progress of scientific research and development. However, maintaining the momentum of research is very important even during times of turmoil. Difficult times demand innovative measures. Implementing well-thought strategies can reduce the impact of a recession on research and help sustain research.
6 Steps to Counter the Effects of Recession on Research
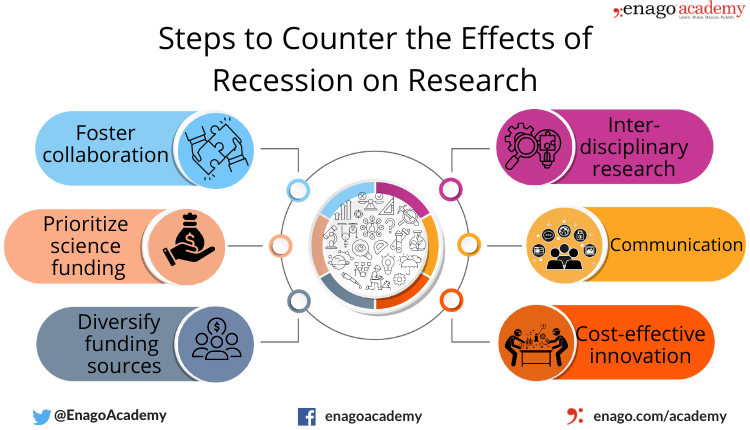
1. Foster collaboration
- Researchers with similar study areas can collaborate irrespective of their social, cultural, and political backgrounds.
- Fostering collaboration between academia and industries can help mitigate the impact of recession.
- Joint initiatives can save a lot of funds and resources, and joint action by the laboratories can expedite research even in the adversity.
2. Prioritize science funding
- Governments and funding agencies should prioritize the allocation of science funding and direct adequate funds to potential projects.
- Policy-makers should advocate the importance of research and protect funding during times of economic downfall.
3. Diversify the funding sources
- Seeking funds from varied sources apart from the government funding bodies can help support research.
- Diversification of funds, combined with collaboration, can help sustain research.
- Promoting international collaborations can also mitigate the lack of funding sources.
4. Interdisciplinary research
- Interdisciplinary research initiatives and collaboration can address pressing issues.
- Combining experts from different disciplines can integrate and attract various funding sources.
- It can also attract funding from sources that power innovative ideas addressing complex problems and bringing change to society.
5. Communication
- Communicating the value of research and enhancing public understanding of its importance can garner public support.
- Researchers can use open blogging platforms to communicate about the difficulties they face during this period. Furthermore, they can use public platforms to enhance their visibility.
- This would increase the commitment among policy-makers and the government to maintain research funding.
- It would also increase the chances of partnership with private organizations, thereby commercializing research.
6. Cost-effective innovation
- Researchers can brain-storm to formulate innovative approaches that can be cost-effective.
- They can plan strategies that offer more results with limited input of resources.
- Additionally, it opens the door for creating new technologies that can have an impact post-recession.
Recessions are unavoidable phases in the economy, accompanied by several downfalls. Though certain experts claim that developed countries will not fall into a recession, ensuring a level of preparedness can help researchers. Research is a long journey and not a sprint, requiring commitment to foresee its potential in the future. Exploring areas of science that hold potential for groundbreaking discoveries requires a high-quality support system. Policy-makers should understand the importance of research and the need for continuous support to keep it alive. Stake-holders must safeguard the future of science and development by making bold decisions and using funds wisely, without hampering the scientific advancements. Adversities should not be a reason to halt research; instead, they should be mitigated through innovation and an improvised approach, resulting in a changing landscape of science.
What do you think about the changing dynamics of research funding? Share your views in form of Thought Pieces, Review Articles, a Study Report, etc. on the other potential impacts of recession in research on Enago Academy Open Platform.










This is very educative